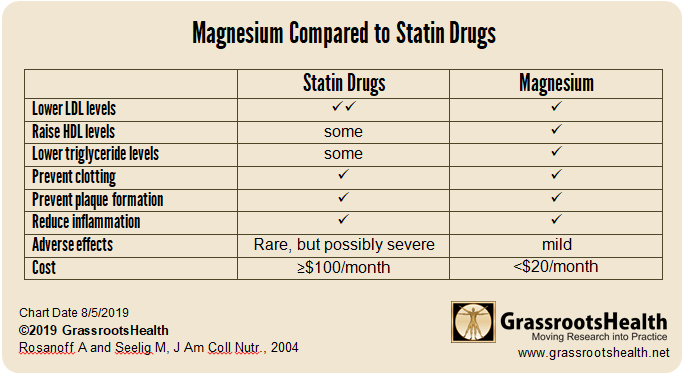Comparing magnesium supplementation with statin drugs
Did you know that magnesium supplementation has some of the same effects on cholesterol as statin drugs?
Greetings!
 |
Did you know that magnesium supplementation has some of the same effects on cholesterol as statin drugs? Today we will highlight key insights from a paper by Andrea Rosanoff and Mildred Seelig which compare the mechanisms and effects of magnesium and statin drugs.
High LDL cholesterol levels, low HDL cholesterol levels, and high triglyceride levels are associated with increased cardiovascular disease risk. In the 1970s and 80s, statin drugs were developed to lower LDL cholesterol levels and prevent cardiovascular disease. Statins work by blocking an enzyme (HMG CoA Reductase) that your body uses to make cholesterol.
Similarly, when there is sufficient magnesium in the body, it works to inactivate this same enzyme though natural control mechanisms. Magnesium is also necessary for another enzyme (LCAT) which lowers LDL and triglyceride levels and raises HDL levels. Further, magnesium activates other enzymes involved in lipid production, such as the conversion of omega-3 and omega-6 into prostaglandins which are important for cardiovascular and general health.
Additionally, both statin drugs and magnesium prevent clotting and atherosclerotic plaques and reduce inflammation. While statins can raise liver enzymes and cause myopathy, a muscle disease resulting in muscular weakness, and cause other side effects, magnesium can protect against myopathy and only has mild gastrointestinal side effects for some. The cost difference is also a differing factor, with statin drugs costing at least $100/month (but may be covered by insurance) compared to magnesium supplements which are less than $20/month.
While statin drugs lower LDL levels more sharply than magnesium, magnesium works through the same pathway to lower LDL levels and more reliably lowers triglycerides and raises HDL, which are also associated with cardiovascular disease. Further, magnesium has similar effects on clotting, plaque formation, and inflammation without the adverse effects and cost associated with statin drugs.